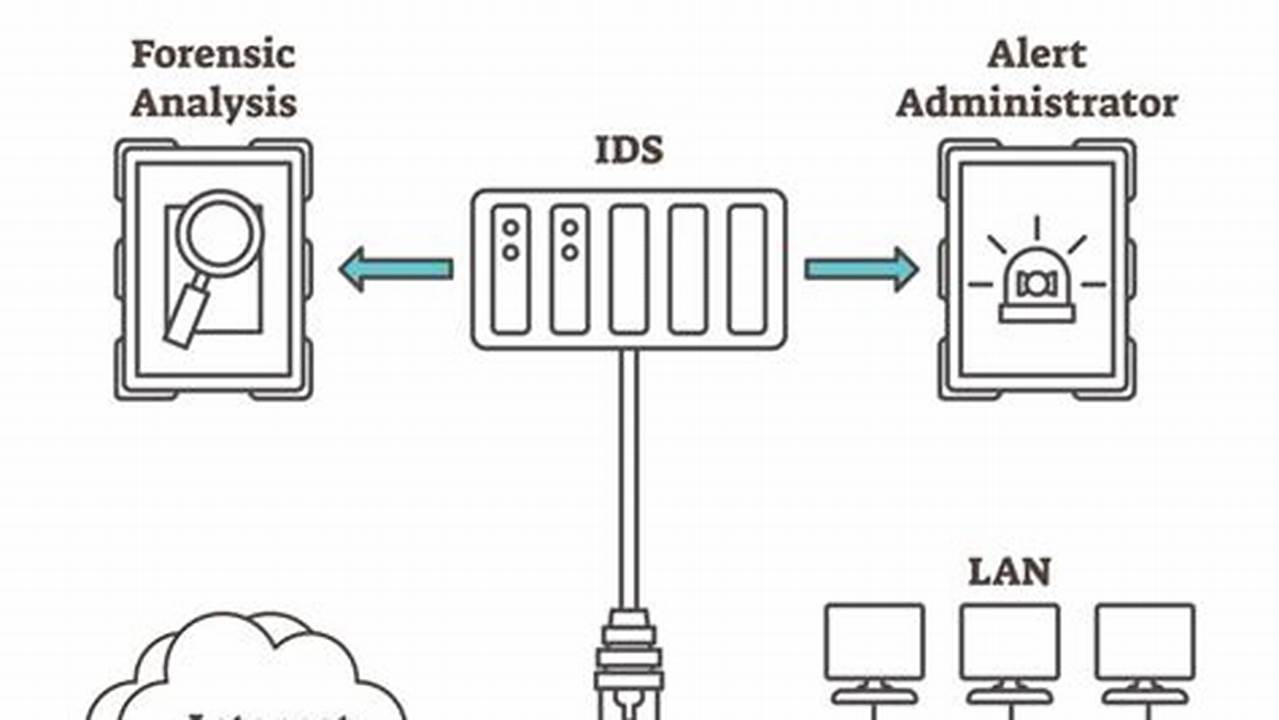
An intrusion detection system (IDS) is a security mechanism used to detect unauthorized access to a computer system or network. It monitors network traffic and system activities for suspicious patterns that may indicate an intrusion attempt. IDS can be hardware-based, software-based, or a combination of both. When an IDS detects a potential intrusion, it can alert administrators and take automated actions to mitigate the threat.
IDS are an important part of a comprehensive security strategy. They can help to identify and respond to threats that may otherwise go unnoticed. IDS can also provide valuable information about the nature of an attack, which can help to improve security measures and prevent future intrusions.
The first IDS were developed in the 1980s. Since then, IDS have become increasingly sophisticated, and they now use a variety of techniques to detect intrusions. These techniques include signature-based detection, anomaly-based detection, and heuristic-based detection.
Intrusion detection system
An intrusion detection system (IDS) is a critical component of any cybersecurity strategy. It plays a vital role in detecting and preventing unauthorized access to computer systems and networks.
- Detection: IDS monitors network traffic and system activities for suspicious patterns that may indicate an intrusion attempt.
- Prevention: IDS can take automated actions to mitigate threats, such as blocking network traffic or shutting down system services.
- Analysis: IDS can provide valuable information about the nature of an attack, which can help to improve security measures and prevent future intrusions.
- Response: IDS can be integrated with other security systems to provide a comprehensive response to security incidents.
- Types: There are two main types of IDS: signature-based and anomaly-based.
- Deployment: IDS can be deployed in a variety of ways, including on-premises, in the cloud, or as a managed service.
These key aspects of IDS are essential for understanding how they work and how they can be used to protect computer systems and networks. By understanding these aspects, organizations can make informed decisions about how to deploy and manage IDS to meet their specific security needs.
Detection
This aspect of IDS is essential for understanding how they work and how they can be used to protect computer systems and networks. By understanding how IDS detect intrusions, organizations can better deploy and manage these systems to meet their specific security needs.
- Pattern recognition: IDS use a variety of techniques to identify suspicious patterns in network traffic and system activities. These techniques include signature-based detection, anomaly-based detection, and heuristic-based detection.
- Real-time monitoring: IDS monitor network traffic and system activities in real time, so that they can detect and respond to intrusions as they occur.
- Threat intelligence: IDS can be integrated with threat intelligence feeds, which provide information about the latest threats and vulnerabilities. This information can help IDS to more effectively detect and prevent intrusions.
- Logging and reporting: IDS can log and report security events, which can help organizations to investigate and respond to security incidents.
These are just a few of the key aspects of IDS detection. By understanding these aspects, organizations can make informed decisions about how to deploy and manage IDS to meet their specific security needs.
Prevention
This aspect of IDS is essential for understanding how they work and how they can be used to protect computer systems and networks. By understanding how IDS prevent intrusions, organizations can better deploy and manage these systems to meet their specific security needs.
IDS can take a variety of automated actions to mitigate threats, including:
- Blocking network traffic: IDS can block network traffic from suspicious sources, such as IP addresses or ports that are known to be associated with malicious activity.
- Shutting down system services: IDS can shut down system services that are being exploited by attackers, such as web servers or database servers.
- Isolating infected systems: IDS can isolate infected systems from the rest of the network, preventing the spread of malware.
- Generating alerts: IDS can generate alerts to notify administrators of potential security incidents.
These are just a few of the ways that IDS can prevent intrusions. By understanding how IDS work, organizations can make informed decisions about how to deploy and manage these systems to meet their specific security needs.
In addition to the benefits listed above, IDS can also help organizations to comply with regulatory requirements, such as the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). These regulations require organizations to implement IDS to protect sensitive data.
Overall, IDS are an essential part of any cybersecurity strategy. They can help organizations to detect, prevent, and respond to security threats. By understanding the different aspects of IDS, organizations can make informed decisions about how to deploy and manage these systems to meet their specific security needs.
Analysis
IDS can provide valuable information about the nature of an attack, which can help to improve security measures and prevent future intrusions. This information can include the type of attack, the source of the attack, and the target of the attack. IDS can also provide information about the attacker’s tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs).
- Identify attack patterns: IDS can help organizations to identify attack patterns and trends. This information can be used to improve security measures and prevent future intrusions.
- Improve security measures: IDS can help organizations to improve their security measures by identifying vulnerabilities and weaknesses in their systems.
- Prevent future intrusions: IDS can help organizations to prevent future intrusions by providing early warning of potential threats.
The analysis capabilities of IDS are essential for organizations that want to improve their security posture and prevent future intrusions. By understanding the nature of attacks, organizations can take steps to protect their systems and data.
Response
Intrusion detection systems (IDS) are an essential part of any cybersecurity strategy. They can detect and prevent unauthorized access to computer systems and networks. However, IDS are not the only security tool that organizations need. In order to effectively protect their systems and data, organizations need to integrate IDS with other security systems to provide a comprehensive response to security incidents.
- Integration with SIEM: IDS can be integrated with security information and event management (SIEM) systems to provide a centralized view of all security events. This allows organizations to correlate events from different sources and identify potential threats that may not be detected by IDS alone.
- Integration with firewalls: IDS can be integrated with firewalls to block network traffic from suspicious sources. This can help to prevent attacks from reaching their target and causing damage.
- Integration with anti-malware: IDS can be integrated with anti-malware systems to detect and remove malware from infected systems. This can help to prevent malware from spreading throughout the network and causing further damage.
- Integration with vulnerability management systems: IDS can be integrated with vulnerability management systems to identify and patch vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers. This can help to prevent attackers from gaining access to systems and networks.
By integrating IDS with other security systems, organizations can create a more comprehensive and effective security posture. This will help to protect their systems and data from a wide range of threats.
Types
Intrusion detection systems (IDS) are security mechanisms used to detect unauthorized access to computer systems and networks. They work by monitoring network traffic and system activities for suspicious patterns that may indicate an intrusion attempt. IDS can be either signature-based or anomaly-based.
Signature-based IDS use a database of known attack signatures to detect intrusions. When an IDS detects a signature that matches a known attack, it generates an alert. Signature-based IDS are effective at detecting known attacks, but they can be ineffective against zero-day attacks, which are new attacks that have not yet been added to the IDS database.
Anomaly-based IDS use statistical models to establish a baseline of normal behavior for a system or network. When the IDS detects activity that deviates from the baseline, it generates an alert. Anomaly-based IDS are effective at detecting zero-day attacks, but they can also generate false positives, which are alerts that are triggered by legitimate activity.
The choice of which type of IDS to use depends on the specific security needs of an organization. Signature-based IDS are more effective at detecting known attacks, while anomaly-based IDS are more effective at detecting zero-day attacks. Many organizations use a combination of both types of IDS to achieve a comprehensive level of protection.
The different types of IDS play a vital role in protecting computer systems and networks from unauthorized access. By understanding the different types of IDS and how they work, organizations can make informed decisions about how to deploy and manage IDS to meet their specific security needs.
Deployment
The deployment of intrusion detection systems (IDS) is a critical aspect of their effectiveness. The method of deployment will depend on a number of factors, including the size and complexity of the network, the security requirements of the organization, and the available resources.
On-premises deployment involves installing and managing IDS on the organization’s own servers. This gives the organization complete control over the IDS, but it also requires the organization to have the necessary expertise and resources to manage the IDS effectively.
Cloud deployment involves deploying IDS in a cloud computing environment. This can be a cost-effective and scalable option for organizations that do not have the resources to manage IDS on-premises. However, cloud deployment can also introduce security risks, such as the risk of data breaches.
Managed service deployment involves outsourcing the management of IDS to a managed security service provider (MSSP). This can be a good option for organizations that do not have the expertise or resources to manage IDS on-premises or in the cloud. However, managed service deployment can also be more expensive than on-premises or cloud deployment.
The choice of deployment method will depend on the specific needs of the organization. Organizations should carefully consider the factors discussed above before making a decision about how to deploy IDS.
The deployment of IDS is an essential part of protecting computer systems and networks from unauthorized access. By understanding the different deployment options, organizations can make informed decisions about how to deploy IDS to meet their specific security needs.
FAQs
Intrusion detection systems (IDS) are an essential part of any cybersecurity strategy, and they can play a vital role in protecting computer systems and networks from unauthorized access. However, there are many common questions and misconceptions about IDS, and it is important to understand the answers to these questions in order to effectively deploy and manage IDS.
Question 1: What is an intrusion detection system (IDS)?
An IDS is a security mechanism used to detect unauthorized access to computer systems and networks. It monitors network traffic and system activities for suspicious patterns that may indicate an intrusion attempt.
Question 2: What are the different types of IDS?
There are two main types of IDS: signature-based and anomaly-based. Signature-based IDS use a database of known attack signatures to detect intrusions. Anomaly-based IDS use statistical models to establish a baseline of normal behavior for a system or network, and they generate alerts when activity deviates from the baseline.
Question 3: How are IDS deployed?
IDS can be deployed in a variety of ways, including on-premises, in the cloud, or as a managed service. On-premises deployment involves installing and managing IDS on the organization’s own servers. Cloud deployment involves deploying IDS in a cloud computing environment. Managed service deployment involves outsourcing the management of IDS to a managed security service provider (MSSP).
Question 4: What are the benefits of using an IDS?
IDS can provide a number of benefits, including the ability to detect and prevent unauthorized access to computer systems and networks, identify attack patterns and trends, improve security measures, and prevent future intrusions.
Question 5: What are the challenges of using an IDS?
There are a number of challenges associated with using an IDS, including the need to manage and maintain the IDS, the potential for false positives, and the risk of IDS evasion.
Question 6: What are the future trends in IDS?
The future of IDS is likely to see increased use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to improve detection accuracy and reduce false positives. IDS is also likely to become more integrated with other security technologies, such as firewalls and anti-malware systems.
Summary:
IDS play an important role in protecting computer systems and networks from unauthorized access. However, it is important to understand the different types of IDS, how they are deployed, and the benefits and challenges associated with using IDS. By understanding these factors, organizations can make informed decisions about how to deploy and manage IDS to meet their specific security needs.
Next:
The next section of this article will provide a more in-depth look at the different types of IDS, their advantages and disadvantages, and how to choose the right IDS for your organization.
Intrusion Detection System Tips
Intrusion detection systems (IDS) are an essential part of any cybersecurity strategy. They can help to detect and prevent unauthorized access to your computer systems and networks. Here are a few tips to help you get the most out of your IDS:
Tip 1: Choose the right IDS for your needs. There are many different types of IDS available, so it is important to choose one that is right for your organization’s specific needs. Consider factors such as the size of your network, the types of threats you are most concerned about, and your budget.
Tip 2: Deploy your IDS correctly. The way you deploy your IDS can have a significant impact on its effectiveness. Be sure to follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully and consider factors such as network topology and traffic patterns.
Tip 3: Manage your IDS effectively. IDS require regular maintenance and updates to stay effective. Be sure to have a plan in place for managing your IDS, including tasks such as signature updates, log monitoring, and performance tuning.
Tip 4: Use IDS data to improve your security posture. IDS can provide valuable insights into the threats that your organization faces. Use this data to improve your security measures and make your network more resilient to attacks.
Tip 5: Integrate IDS with other security technologies. IDS can be more effective when integrated with other security technologies, such as firewalls, anti-malware, and SIEM systems. This allows you to create a more comprehensive security solution that can better protect your organization from threats.
Summary:
By following these tips, you can improve the effectiveness of your IDS and better protect your organization from cyber threats.
Next:
The next section of this article will provide a more in-depth look at the different types of IDS, their advantages and disadvantages, and how to choose the right IDS for your organization.
Conclusion
Intrusion detection systems (IDS) are a critical part of any cybersecurity strategy. They can help to detect and prevent unauthorized access to computer systems and networks, and they can provide valuable insights into the threats that an organization faces.
In this article, we have explored the different types of IDS, their advantages and disadvantages, and how to choose the right IDS for an organization’s specific needs. We have also provided tips for deploying, managing, and using IDS effectively.
By understanding the importance of IDS and how to use them effectively, organizations can improve their security posture and better protect themselves from cyber threats.
Youtube Video: