Incident detection and response is the process of identifying and responding to security incidents. It involves detecting suspicious activity, investigating the incident, and taking steps to mitigate the damage and prevent future incidents. Incident detection and response is a critical part of any security program, as it helps organizations to quickly and effectively respond to security threats.
Incident detection and response can be divided into four main phases: preparation, detection, analysis, and response. During the preparation phase, organizations develop an incident response plan and train their staff on how to respond to an incident. The detection phase involves monitoring systems for suspicious activity and identifying potential incidents. The analysis phase involves investigating the incident to determine its scope and impact. The response phase involves taking steps to mitigate the damage and prevent future incidents.
Incident detection and response is a complex and challenging process, but it is essential for organizations to protect themselves from security threats. By implementing a robust incident detection and response program, organizations can quickly and effectively respond to incidents and minimize their impact.
Incident detection and response
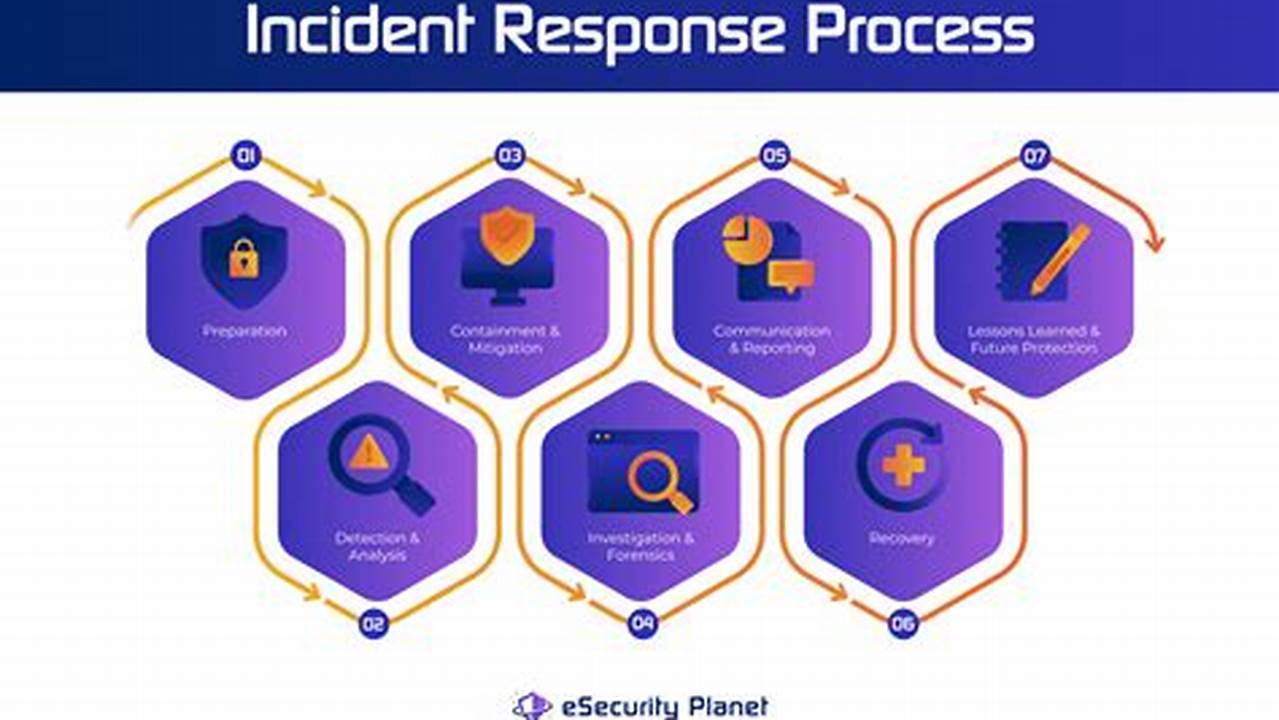
Incident detection and response (IDR) is a critical part of any organization’s security program. It involves the processes and technologies used to identify, investigate, and respond to security incidents.
- Detection: Identifying suspicious activity and potential incidents.
- Investigation: Determining the scope and impact of an incident.
- Response: Taking steps to mitigate the damage and prevent future incidents.
- Planning: Developing an incident response plan and training staff.
- Analysis: Reviewing incident data to identify trends and improve response capabilities.
- Communication: Sharing information about incidents with stakeholders.
- Recovery: Restoring systems and data after an incident.
These key aspects of IDR are all essential for organizations to effectively protect themselves from security threats. By implementing a robust IDR program, organizations can quickly and effectively respond to incidents and minimize their impact.
For example, a recent study by the Ponemon Institute found that organizations with a mature IDR program were able to reduce the average cost of a data breach by 35%. Additionally, organizations with a mature IDR program were more likely to be able to contain a data breach within 30 days.
IDR is a complex and challenging process, but it is essential for organizations to protect themselves from security threats. By understanding the key aspects of IDR and implementing a robust IDR program, organizations can improve their ability to detect, investigate, and respond to security incidents.
Detection
Detection is the first step in the incident detection and response (IDR) process. It involves identifying suspicious activity and potential incidents that may require further investigation. Detection can be done through a variety of methods, including:
- Security monitoring: Monitoring systems and networks for suspicious activity, such as unauthorized access attempts, malware infections, or data breaches.
- Log analysis: Analyzing system logs to identify suspicious activity, such as failed login attempts, changes to critical files, or unusual network traffic.
- Intrusion detection systems (IDS): Detecting and alerting on suspicious network activity, such as port scans, denial-of-service attacks, or malware infections.
- User behavior analytics (UBA): Analyzing user behavior to identify anomalous activity, such as accessing sensitive data without authorization or making excessive changes to system configurations.
Detection is a critical part of the IDR process, as it allows organizations to quickly identify and respond to potential security incidents. By implementing effective detection mechanisms, organizations can reduce the risk of a security incident and minimize the impact if one does occur.
Investigation
Investigation is a critical part of the incident detection and response (IDR) process. It involves determining the scope and impact of an incident, which is essential for developing an effective response plan. The investigation process typically includes the following steps:
- Containment: Isolating the affected systems and data to prevent the incident from spreading.
- Identification: Determining the type of incident that has occurred, such as a data breach, malware infection, or denial-of-service attack.
- Analysis: Gathering evidence and analyzing the incident to determine its root cause and impact.
- Remediation: Taking steps to mitigate the damage caused by the incident and prevent future incidents from occurring.
Investigation is a complex and challenging process, but it is essential for organizations to effectively respond to security incidents. By conducting a thorough investigation, organizations can quickly and effectively contain the incident, minimize the damage, and prevent future incidents from occurring.
Response
Response is a critical part of the incident detection and response (IDR) process. It involves taking steps to mitigate the damage caused by an incident and prevent future incidents from occurring. The response process typically includes the following steps:
- Containment: Isolating the affected systems and data to prevent the incident from spreading.
- Eradication: Removing the malicious software or other threat that caused the incident.
- Recovery: Restoring the affected systems and data to their normal state.
- Lessons learned: Identifying the root cause of the incident and implementing measures to prevent future incidents from occurring.
Response is a complex and challenging process, but it is essential for organizations to effectively respond to security incidents. By taking the appropriate steps to mitigate the damage and prevent future incidents, organizations can minimize the impact of security incidents and protect their critical assets.
For example, in the case of a data breach, the response process may involve containing the breach by isolating the affected systems, eradicating the malware that caused the breach, recovering the affected data, and implementing measures to prevent future breaches from occurring. This may involve implementing new security controls, such as firewalls or intrusion detection systems, or educating employees about the importance of cybersecurity.
By understanding the importance of response as a component of IDR and implementing effective response measures, organizations can improve their ability to protect themselves from security threats and minimize the impact of security incidents.
Planning
Planning is a critical part of the incident detection and response (IDR) process. It involves developing an incident response plan and training staff on how to respond to an incident. An incident response plan outlines the steps that should be taken in the event of an incident, including roles and responsibilities, communication protocols, and containment and recovery procedures.
Training staff on the incident response plan is essential to ensure that everyone knows what to do in the event of an incident. Training should cover the following topics:
- The incident response plan
- Roles and responsibilities
- Communication protocols
- Containment and recovery procedures
Planning and training are essential components of an effective IDR program. By developing an incident response plan and training staff on how to respond to an incident, organizations can improve their ability to quickly and effectively respond to security incidents and minimize their impact.
For example, in the case of a data breach, an organization with a well-developed incident response plan and trained staff will be able to quickly contain the breach, eradicate the malware that caused the breach, and recover the affected data. This will help to minimize the impact of the breach and protect the organization’s critical assets.
Planning and training are essential components of an effective IDR program. By investing in planning and training, organizations can improve their ability to protect themselves from security threats and minimize the impact of security incidents.
Analysis
Analysis is a critical component of incident detection and response (IDR) as it allows organizations to identify trends and improve their response capabilities. By reviewing incident data, organizations can gain insights into the types of incidents they are most likely to face, the root causes of those incidents, and the effectiveness of their response measures.
This information can then be used to improve the organization’s IDR program by identifying areas for improvement and implementing new or revised policies and procedures. For example, if an organization finds that they are frequently experiencing data breaches, they may need to implement additional security controls or provide additional training to their staff on cybersecurity best practices.
Analysis is also essential for keeping up with the evolving threat landscape. As new threats emerge, it is important to review incident data to identify any new trends or patterns. This information can then be used to develop new or revised response measures to protect the organization from these new threats.
By continuously reviewing incident data and identifying trends, organizations can improve their ability to detect and respond to security incidents and minimize their impact.
Communication
Communication is a critical component of incident detection and response (IDR). It involves sharing information about incidents with stakeholders, including employees, customers, partners, and the media. Effective communication is essential for ensuring that everyone is aware of the incident, understands the impact, and knows what to do.
There are several reasons why communication is important in IDR. First, it helps to ensure that everyone is aware of the incident and understands the impact. This is important for making informed decisions about how to respond to the incident and for minimizing the damage. Second, communication helps to coordinate the response effort. By sharing information about the incident, stakeholders can work together to develop and implement a response plan. Third, communication helps to build trust and credibility with stakeholders. By being transparent and open about the incident, organizations can show that they are committed to protecting their stakeholders’ interests.
There are several best practices for communicating about incidents with stakeholders. First, it is important to be clear and concise in your communication. Stakeholders need to be able to quickly and easily understand what happened, the impact of the incident, and what is being done to respond. Second, it is important to be timely in your communication. Stakeholders need to be informed about the incident as soon as possible so that they can take appropriate action. Third, it is important to be accurate in your communication. Stakeholders need to be able to trust the information that you are providing them. Fourth, it is important to be sensitive in your communication. Stakeholders may be feeling anxious or concerned about the incident, so it is important to be respectful and understanding in your communication.
Effective communication is essential for incident detection and response. By sharing information about incidents with stakeholders, organizations can ensure that everyone is aware of the incident, understands the impact, and knows what to do. This helps to coordinate the response effort, build trust and credibility with stakeholders, and minimize the damage caused by the incident.
Recovery
Recovery is a critical component of incident detection and response (IDR). It involves restoring systems and data after an incident has occurred. The goal of recovery is to restore the organization to its normal state of operation as quickly as possible and with minimal loss of data or functionality.
There are several reasons why recovery is important in IDR. First, it helps to minimize the damage caused by an incident. By restoring systems and data, organizations can quickly get back to business and continue operating normally. Second, recovery helps to prevent future incidents from occurring. By identifying and fixing the root cause of an incident, organizations can prevent similar incidents from happening in the future. Third, recovery helps to build trust and credibility with stakeholders. By being able to quickly and effectively recover from an incident, organizations can show that they are committed to protecting their stakeholders’ interests.
There are several best practices for recovering from an incident. First, it is important to have a disaster recovery plan in place. A disaster recovery plan outlines the steps that need to be taken to recover from an incident, including roles and responsibilities, communication protocols, and recovery procedures. Second, it is important to test your disaster recovery plan regularly. This will help to ensure that the plan is up to date and that everyone knows what to do in the event of an incident. Third, it is important to have the necessary resources in place to recover from an incident. This includes having the necessary hardware, software, and personnel.
Effective recovery is essential for incident detection and response. By restoring systems and data after an incident, organizations can minimize the damage, prevent future incidents from occurring, and build trust and credibility with stakeholders.
For example, in the case of a data breach, recovery may involve restoring the affected data from a backup. This may also involve implementing additional security controls to prevent future breaches from occurring. By having a disaster recovery plan in place and testing it regularly, organizations can quickly and effectively recover from an incident and minimize the damage.
Recovery is a complex and challenging process, but it is essential for organizations to protect themselves from security threats. By understanding the importance of recovery as a component of IDR and implementing effective recovery measures, organizations can improve their ability to respond to security incidents and minimize their impact.
Frequently Asked Questions on Incident Detection and Response
This section provides answers to some of the most frequently asked questions about incident detection and response (IDR).
Question 1: What is incident detection and response (IDR)?
Answer: IDR is the process of identifying, investigating, and responding to security incidents.
Question 2: Why is IDR important?
Answer: IDR is important because it helps organizations to quickly and effectively respond to security incidents, minimizing the damage and preventing future incidents from occurring.
Question 3: What are the key components of an IDR program?
Answer: The key components of an IDR program include detection, investigation, response, planning, analysis, communication, and recovery.
Question 4: What are some best practices for implementing an IDR program?
Answer: Some best practices for implementing an IDR program include developing an incident response plan, training staff, conducting regular exercises, and reviewing incident data to identify trends and improve response capabilities.
Question 5: What are some common challenges associated with IDR?
Answer: Some common challenges associated with IDR include the need to keep up with the evolving threat landscape, the need to coordinate between different teams and departments, and the need to balance the need for security with the need for business continuity.
Question 6: What are some emerging trends in IDR?
Answer: Some emerging trends in IDR include the use of artificial intelligence and machine learning to automate detection and response tasks, the use of cloud-based technologies to improve scalability and flexibility, and the use of managed security services to provide expertise and support.
Summary:
IDR is a critical component of any organization’s security program. By understanding the importance of IDR and implementing an effective IDR program, organizations can improve their ability to protect themselves from security threats and minimize the impact of security incidents.
Transition to the next article section:
The next section of this article will discuss some of the specific challenges associated with IDR in the cloud.
Incident Detection and Response Best Practices
Effective incident detection and response (IDR) is crucial for protecting organizations from cyber threats. Here are some essential tips to enhance your IDR capabilities:
Tip 1: Develop a Comprehensive Incident Response Plan
Establish a clear and detailed plan outlining roles, responsibilities, communication protocols, and response procedures for various types of security incidents.
Tip 2: Implement Robust Security Monitoring and Detection Tools
Deploy advanced security tools, such as intrusion detection systems (IDS) and security information and event management (SIEM) solutions, to continuously monitor network traffic and identify suspicious activities in real-time.
Tip 3: Train and Educate Your Team Regularly
Provide regular training to your team on incident response procedures, threat detection techniques, and best practices. Empower them with the knowledge and skills to effectively respond to security incidents.
Tip 4: Conduct Regular Incident Response Exercises
Simulate security incidents to test your response plan, identify areas for improvement, and enhance the overall readiness of your team.
Tip 5: Foster Collaboration and Information Sharing
Establish clear communication channels and foster collaboration among IT, security, and business teams. Facilitate the sharing of threat intelligence and best practices to improve overall cybersecurity posture.
Tip 6: Leverage Automation and Orchestration
Utilize automation tools to streamline incident response tasks, such as containment, notification, and remediation. Orchestrate security tools to enable automated workflows and improve response efficiency.
Tip 7: Continuously Monitor and Improve Your IDR Program
Regularly review incident data, identify trends, and make adjustments to your IDR program to enhance its effectiveness and stay ahead of evolving threats.
Summary:
By implementing these best practices, organizations can strengthen their IDR capabilities, minimize the impact of security incidents, and enhance their overall cybersecurity posture.
Transition to the conclusion:
Effective incident detection and response is a continuous journey. By adopting these tips and continuously improving your program, you can significantly enhance your organization’s resilience to cyber threats.
Conclusion
Incident detection and response (IDR) is a critical component of any organization’s cybersecurity strategy. By effectively detecting, investigating, and responding to security incidents, organizations can minimize the impact of cyber threats and protect their sensitive data, systems, and reputation.
This article has explored the key aspects of IDR, including detection, investigation, response, planning, analysis, communication, and recovery. We have discussed best practices for implementing an effective IDR program, such as developing a comprehensive incident response plan, implementing robust security monitoring tools, and training and educating the team.
By embracing the principles of IDR and continuously improving your program, you can significantly enhance your organization’s resilience to cyber threats. Remember, effective IDR is an ongoing journey, and it requires the commitment and collaboration of the entire organization to stay ahead of evolving threats and protect your critical assets.
Youtube Video: