Ultimate Guide to Host-Based Security Systems for Enhanced Cybersecurity
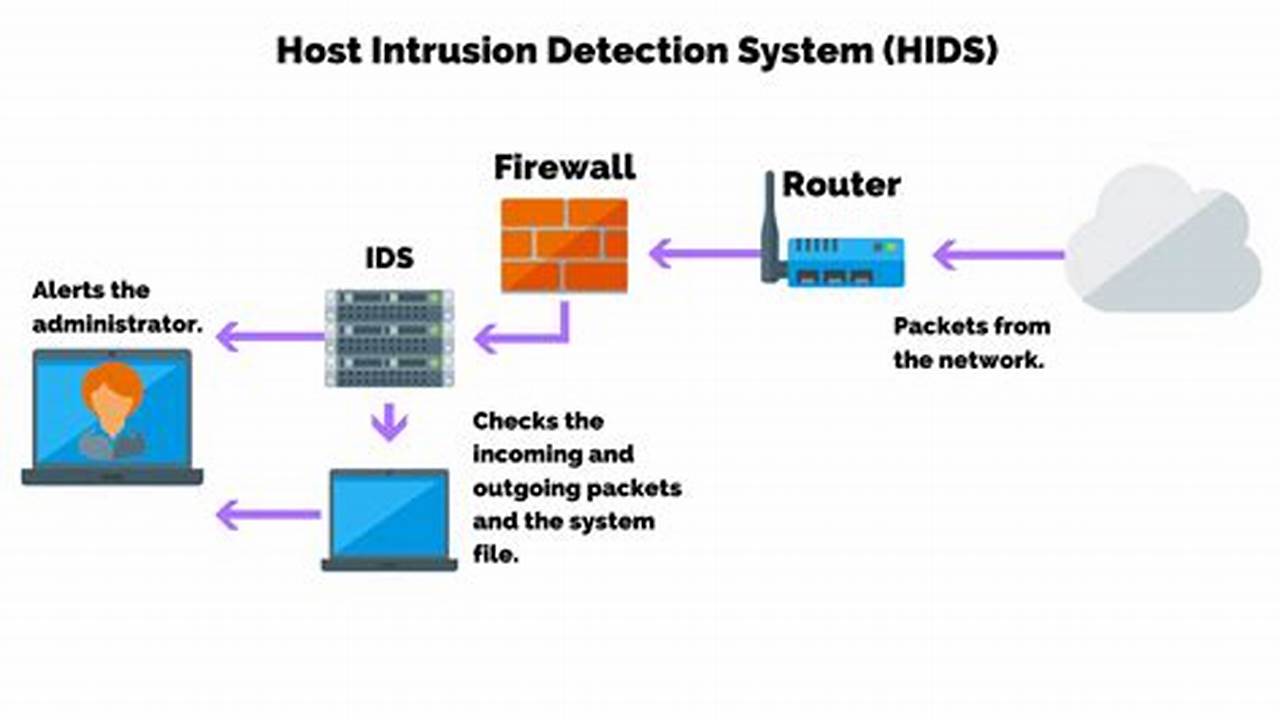
A host-based security system is a type of security system that is installed on a computer or other device. It is designed to protect the device from unauthorized access, malware, and other threats. Host-based security systems can include a variety of features, such as firewalls, antivirus software, and intrusion detection systems.
Host-based security systems are important because they can help to protect devices from a variety of threats. They can also help to ensure that devices are compliant with security policies. Host-based security systems have been used for many years, and they have evolved over time to meet the changing needs of users.
The main topics that will be covered in this article include:
- The different types of host-based security systems
- The benefits of using a host-based security system
- The challenges of using a host-based security system
- The future of host-based security systems
Host-based security system
Host-based security systems are an essential part of any comprehensive security strategy. They can help to protect devices from a variety of threats, including malware, unauthorized access, and data breaches. Here are eight key aspects of host-based security systems:
- Protection: Host-based security systems can protect devices from a variety of threats, including malware, unauthorized access, and data breaches.
- Prevention: Host-based security systems can help to prevent threats from reaching devices in the first place.
- Detection: Host-based security systems can detect threats that have already reached devices.
- Response: Host-based security systems can respond to threats by taking actions such as blocking access to malicious websites or quarantining infected files.
- Monitoring: Host-based security systems can monitor devices for suspicious activity.
- Reporting: Host-based security systems can report security events to administrators.
- Management: Host-based security systems can be managed centrally, making it easy to deploy and update security policies.
- Scalability: Host-based security systems can be scaled to meet the needs of any organization.
These eight key aspects of host-based security systems make them an essential part of any comprehensive security strategy. By implementing a host-based security system, organizations can help to protect their devices from a variety of threats and ensure that their data is safe.
Protection
Host-based security systems provide comprehensive protection for devices against a wide range of threats. They safeguard systems from malicious software, unauthorized access attempts, and data breaches, ensuring the integrity and security of sensitive information.
- Malware Protection: Host-based security systems employ advanced malware detection and prevention mechanisms to identify and neutralize malicious software, such as viruses, spyware, and ransomware. They monitor system activity for suspicious behavior, preventing malware from infecting and damaging devices.
- Unauthorized Access Prevention: These systems implement robust access control measures to prevent unauthorized users from gaining access to devices and sensitive data. They utilize authentication mechanisms, such as passwords, biometrics, and multi-factor authentication, to verify the identity of users and restrict access to authorized personnel only.
- Data Breach Prevention: Host-based security systems play a crucial role in preventing data breaches by safeguarding sensitive information stored on devices. They employ encryption technologies to protect data at rest and in transit, ensuring its confidentiality and integrity. Additionally, they monitor data access patterns and flag any suspicious activities that may indicate a potential breach.
By providing these protective measures, host-based security systems serve as a vital defense mechanism for devices, safeguarding them from a constantly evolving threat landscape. They empower organizations and individuals to protect their critical assets and maintain the security of their systems.
Prevention
Host-based security systems are designed to prevent threats from reaching devices in the first place, forming a proactive defense mechanism against cyberattacks. They employ various techniques to safeguard devices from malicious actors and protect critical data.
-
Network Perimeter Protection:
Host-based security systems establish a strong network perimeter defense by implementing firewalls and intrusion detection/prevention systems (IDS/IPS). These tools monitor incoming and outgoing network traffic, blocking unauthorized access attempts and preventing malicious traffic from reaching devices. -
Vulnerability Management:
They continuously scan devices for vulnerabilities and apply security patches promptly. By addressing vulnerabilities, host-based security systems reduce the attack surface and make it harder for attackers to exploit weaknesses in software or operating systems. -
Application Control:
Host-based security systems enforce application control policies to restrict the execution of unauthorized or malicious software. They prevent untrusted applications from running and limit user privileges, minimizing the risk of malware infections. -
Behavior Monitoring:
These systems monitor device behavior for anomalies and suspicious activities. They use advanced algorithms and machine learning techniques to detect deviations from normal patterns, identifying potential threats in real-time and responding accordingly.
The preventive measures employed by host-based security systems are crucial for safeguarding devices and data in today’s dynamic threat landscape. By blocking threats before they reach devices, these systems significantly reduce the risk of successful cyberattacks, ensuring the integrity and security of critical assets.
Detection
The ability to detect threats that have already reached devices is a critical component of host-based security systems. Traditional security measures focus on preventing threats from reaching devices in the first place, but in today’s complex threat landscape, it is inevitable that some threats will evade these defenses. Host-based security systems provide an additional layer of protection by detecting these threats once they have breached the perimeter.
Detection capabilities are essential for several reasons. First, they enable organizations to identify and respond to threats that may have bypassed other security controls. Second, they provide early warning of potential attacks, allowing organizations to take steps to mitigate the impact of a breach. Third, detection capabilities can help organizations to identify the source of an attack, which can be valuable for forensic investigations and future prevention efforts.
Host-based security systems use a variety of techniques to detect threats, including:
- File integrity monitoring
- Behavior-based detection
- Network traffic analysis
- Machine learning
These techniques work together to provide a comprehensive view of device activity, allowing host-based security systems to detect even the most sophisticated threats.
The detection capabilities of host-based security systems are essential for protecting organizations from a wide range of threats. By detecting threats that have already reached devices, host-based security systems help to reduce the risk of data breaches, financial loss, and reputational damage.
Response
The response capabilities of host-based security systems are critical for protecting devices and data from threats that have already reached the device. These systems can take a variety of actions to respond to threats, including:
- Blocking access to malicious websites
- Quarantining infected files
- Terminating malicious processes
- Rolling back changes made by malware
The ability to respond to threats quickly and effectively is essential for minimizing the impact of a breach. By taking immediate action to contain and neutralize threats, host-based security systems can help to prevent data loss, financial loss, and reputational damage.
One of the most important aspects of response is the ability to block access to malicious websites. Malicious websites can be used to distribute malware, steal sensitive information, or launch phishing attacks. By blocking access to these websites, host-based security systems can help to prevent these threats from reaching devices.
Another important aspect of response is the ability to quarantine infected files. Infected files can spread malware to other files and systems on the network. By quarantining infected files, host-based security systems can help to prevent the spread of malware and protect other devices on the network.
The response capabilities of host-based security systems are essential for protecting devices and data from threats. By taking immediate action to contain and neutralize threats, these systems can help to minimize the impact of a breach.
Monitoring
Monitoring is a crucial aspect of host-based security systems, as it allows them to detect and respond to suspicious activity on devices. By continuously monitoring devices for suspicious activity, host-based security systems can help to prevent threats from escalating and causing damage.
There are a variety of ways that host-based security systems can monitor devices for suspicious activity, including:
- File integrity monitoring
- Behavior-based detection
- Network traffic analysis
- Machine learning
File integrity monitoring monitors files for changes that may indicate that they have been infected with malware. Behavior-based detection monitors devices for suspicious behavior, such as processes that are attempting to access sensitive data or that are behaving in an unusual way. Network traffic analysis monitors network traffic for suspicious activity, such as attempts to connect to known malicious websites or to transfer sensitive data to unauthorized locations. Machine learning can be used to detect suspicious activity by identifying patterns that are not easily detectable by traditional methods.
The information that is collected by host-based security systems can be used to generate alerts, which can be sent to administrators or security analysts for further investigation. This information can also be used to create reports that can be used to track trends and to identify areas where security can be improved.
Monitoring is an essential component of host-based security systems, as it allows them to detect and respond to suspicious activity on devices. By continuously monitoring devices for suspicious activity, host-based security systems can help to prevent threats from escalating and causing damage.
Reporting
Reporting is an essential aspect of host-based security systems, as it allows administrators to stay informed about the security status of their devices and to take appropriate action in the event of a security event.
- Security Event Detection: Host-based security systems monitor devices for suspicious activity and security events. When a security event is detected, the system generates an alert and sends it to the administrator.
- Alert Notification: Alerts can be sent via email, SMS, or other methods to ensure that the administrator is notified promptly. This allows the administrator to take immediate action to investigate and respond to the security event.
- Centralized Reporting: Host-based security systems can be configured to send reports to a centralized server. This allows administrators to view all security events from multiple devices in one place, making it easier to identify trends and patterns.
- Compliance Reporting: Host-based security systems can generate reports that demonstrate compliance with security regulations and standards. This can be useful for organizations that are required to meet specific compliance requirements.
Reporting is an essential component of host-based security systems, as it provides administrators with the information they need to protect their devices and data from threats. By providing timely and detailed reports on security events, host-based security systems help administrators to maintain a strong security posture and to respond quickly and effectively to security incidents.
Management
Centralized management is a critical component of host-based security systems, enabling efficient deployment and updates of security policies across multiple devices. It simplifies the administration and maintenance of security measures, ensuring consistent protection for all endpoints.
The ability to manage host-based security systems centrally offers several advantages. Firstly, it eliminates the need for manual configuration and updates on individual devices, saving time and reducing the risk of errors. Secondly, centralized management provides a comprehensive view of the security posture of all devices, allowing administrators to quickly identify and address any vulnerabilities or threats.
For example, in a large enterprise with thousands of endpoints, deploying and updating security policies manually would be a daunting task. Centralized management allows administrators to push updates and configurations to all devices simultaneously, ensuring that all endpoints are protected with the latest security measures. This streamlined approach significantly reduces the risk of security breaches and ensures compliance with industry regulations.
Moreover, centralized management facilitates the implementation of consistent security policies across the organization. By defining and enforcing security policies centrally, administrators can ensure that all devices adhere to the same level of protection, regardless of their location or user. This consistency is essential for maintaining a strong security posture and preventing unauthorized access or data breaches.
In summary, the centralized management of host-based security systems is a crucial aspect of comprehensive security strategies. It enables efficient deployment and updates of security policies, provides a holistic view of the security posture, and ensures consistent protection across all endpoints. By leveraging centralized management capabilities, organizations can significantly enhance their security posture, reduce the risk of breaches, and simplify the administration of their security systems.
Scalability
The scalability of host-based security systems is a critical factor for organizations of all sizes. As organizations grow and their IT environments become more complex, they need a security solution that can scale to meet their evolving needs. Host-based security systems are designed to be scalable, allowing organizations to add or remove devices as needed without compromising security.
- Centralized Management: Host-based security systems can be centrally managed, making it easy to deploy and update security policies across multiple devices. This centralized management allows organizations to scale their security systems quickly and efficiently, ensuring that all devices are protected with the latest security updates.
- Flexible Deployment Options: Host-based security systems can be deployed on a variety of devices, including physical servers, virtual machines, and cloud-based instances. This flexibility allows organizations to scale their security systems to meet the needs of their specific IT environment.
- Cloud-Based Scalability: Host-based security systems can be deployed in the cloud, which provides organizations with the ability to scale their security systems on demand. This scalability is essential for organizations that experience seasonal fluctuations in traffic or that need to quickly add capacity to meet unexpected demand.
- Cost-Effective Scalability: Host-based security systems are a cost-effective way to scale security. By deploying host-based security systems, organizations can avoid the need to purchase and manage additional hardware and software, which can save money and reduce complexity.
The scalability of host-based security systems is a key factor for organizations of all sizes. By choosing a host-based security system that is scalable, organizations can ensure that their security systems will be able to meet their evolving needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
This section addresses common questions and misconceptions about host-based security systems.
Question 1: What are the main benefits of using a host-based security system?
Host-based security systems offer a range of benefits, including protection against malware, unauthorized access, data breaches, and other threats. They provide real-time monitoring, detection, and response capabilities, ensuring comprehensive security for individual devices.
Question 2: How do host-based security systems differ from network-based security systems?
Host-based security systems focus on protecting individual devices, while network-based security systems protect the entire network. Host-based systems monitor and secure devices at the endpoint level, offering a more granular level of protection compared to network-based systems, which monitor and secure traffic at the network level.
Question 3: Are host-based security systems effective against sophisticated cyber threats?
Yes, host-based security systems are designed to detect and mitigate sophisticated cyber threats. They employ advanced techniques such as machine learning and behavior-based detection to identify and neutralize zero-day attacks, malware, and other emerging threats.
Question 4: Can host-based security systems be deployed on all types of devices?
Host-based security systems can be deployed on a wide range of devices, including physical servers, virtual machines, cloud instances, and endpoint devices such as laptops and smartphones. Their versatility makes them suitable for protecting diverse IT environments.
Question 5: Are host-based security systems expensive to implement and maintain?
The cost of implementing and maintaining host-based security systems varies depending on the specific solution and the number of devices being protected. However, these systems offer a cost-effective way to enhance security, as they eliminate the need for additional hardware and software, and provide centralized management capabilities.
Question 6: How can organizations ensure the effectiveness of their host-based security systems?
Organizations can ensure the effectiveness of their host-based security systems by implementing best practices such as regular security updates, monitoring and analyzing security logs, conducting vulnerability assessments, and providing ongoing training to users on cybersecurity awareness.
In summary, host-based security systems play a crucial role in protecting individual devices from a wide range of threats. Their scalability, flexibility, and advanced detection and response capabilities make them essential for organizations seeking to enhance their overall cybersecurity posture.
Transition to the next article section: Host-based security systems are a vital component of a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy. By leveraging their capabilities, organizations can effectively safeguard their devices and data from malicious actors and evolving threats.
Host-based Security System Tips
Implement robust host-based security systems to safeguard your devices and data from a wide range of threats. Here are some essential tips to enhance the effectiveness of your host-based security measures:
Tip 1: Deploy Multi-layered Security: Implement a combination of host-based security tools, including antivirus software, firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions, to provide comprehensive protection against various threats.
Tip 2: Enforce Patch Management: Regularly update operating systems, software, and applications with the latest security patches to address vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers.
Tip 3: Configure Secure Settings: Harden host-based security configurations, such as disabling unnecessary services, restricting user privileges, and implementing strong password policies, to reduce the attack surface.
Tip 4: Monitor System Activity: Continuously monitor system logs and activity for any suspicious or unusual events that may indicate malicious activity or security breaches.
Tip 5: Educate Users: Provide regular cybersecurity awareness training to users to educate them on best practices, such as avoiding phishing scams, recognizing social engineering attempts, and reporting suspicious activity.
Tip 6: Implement Data Backup and Recovery: Establish a robust data backup and recovery plan to protect critical data from loss due to security incidents, hardware failures, or natural disasters.
Tip 7: Conduct Regular Security Audits: Periodically perform security audits to assess the effectiveness of your host-based security measures, identify vulnerabilities, and make necessary improvements.
By following these tips, you can significantly enhance the security posture of your systems and protect your organization from the evolving threat landscape.
Host-based Security Systems
Host-based security systems serve as a critical foundation for protecting individual devices and safeguarding data in today’s interconnected digital world. Throughout this article, we have explored the multifaceted nature of host-based security systems, examining their capabilities, benefits, and essential components.
Host-based security systems provide comprehensive protection against a wide spectrum of threats, including malware, unauthorized access, data breaches, and sophisticated cyberattacks. Their ability to monitor, detect, and respond to these threats in real-time makes them an indispensable tool for organizations seeking to enhance their cybersecurity posture.
As the threat landscape continues to evolve, host-based security systems will remain a cornerstone of cybersecurity strategies. By implementing robust host-based security measures and adhering to best practices, organizations can effectively safeguard their devices, data, and reputation from malicious actors and evolving threats.
Youtube Video:
