Secure Your Endpoints: A Comprehensive Guide to Endpoint Risk Management
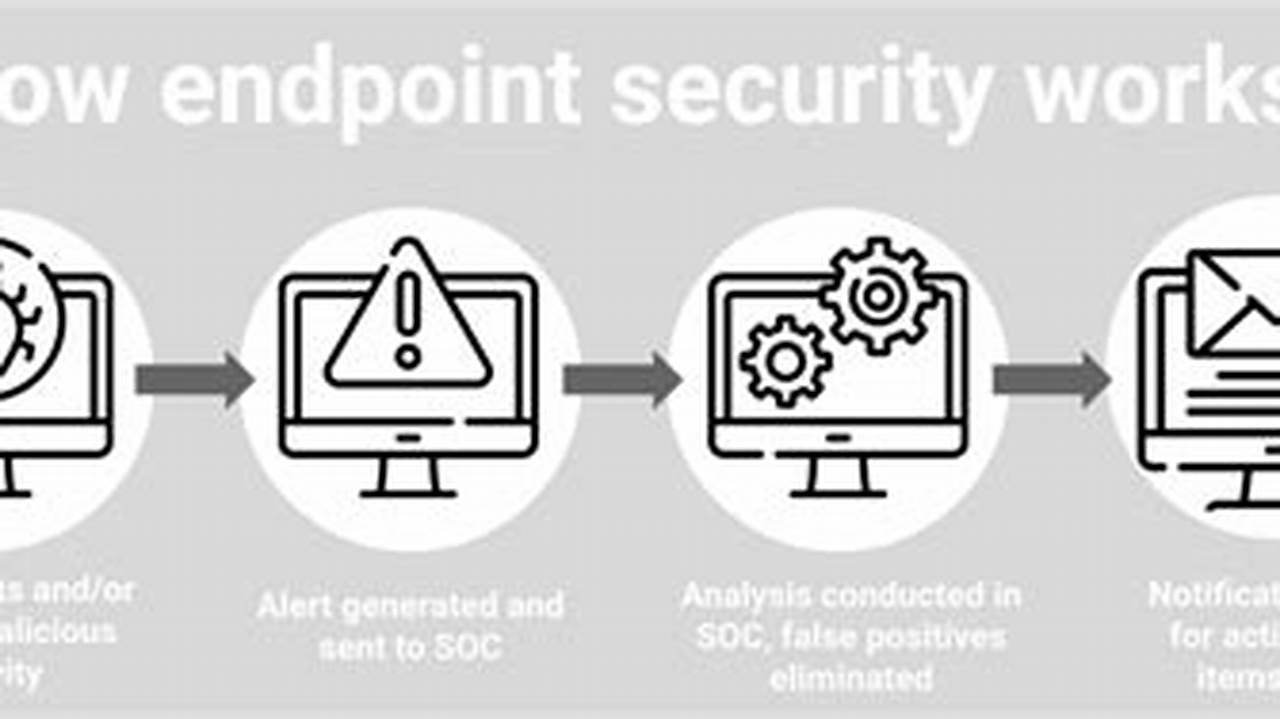
Endpoint risk management refers to the strategies and practices employed to identify, assess, mitigate, and monitor risks associated with endpointdevices. Endpoint devices are any devices that connect to a network, such as laptops, desktops, smartphones, and Internet of Things (IoT) devices. Endpoint risk management aims to protect these devices from unauthorized access, data breaches, malware infections, and other threats.
Effective endpoint risk management is crucial for organizations of all sizes. By implementing robust endpoint security measures, organizations can safeguard sensitive data, maintain regulatory compliance, and minimize the impact of cyberattacks. Endpoint risk management involves implementing security controls such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, antivirus software, and endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools. It also includes regular security updates, employee training, and vulnerability management.
Endpoint risk management is an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring and adaptation to the evolving threat landscape. By proactively managing endpoint risks, organizations can significantly reduce the likelihood and impact of cyberattacks, protecting their critical assets and maintaining business continuity.
Endpoint risk management
Endpoint risk management encompasses a range of essential aspects that are crucial for safeguarding endpoint devices from various threats and vulnerabilities. These key aspects include:
- Identification: Recognizing and classifying potential risks to endpoints.
- Assessment: Evaluating the likelihood and impact of identified risks.
- Mitigation: Implementing controls and measures to reduce the severity or likelihood of risks.
- Monitoring: Continuously tracking and observing endpoints for suspicious activities or vulnerabilities.
- Response: Taking appropriate actions to address and contain threats or incidents.
- Recovery: Restoring systems and data to a functional state after an incident.
These aspects are interconnected and interdependent, forming a comprehensive approach to endpoint risk management. By effectively addressing these key areas, organizations can significantly enhance their endpoint security posture, protect sensitive data, and maintain business continuity.
Identification: Recognizing and classifying potential risks to endpoints.
The identification of potential risks to endpoints is a critical component of endpoint risk management. It involves recognizing and categorizing the various threats and vulnerabilities that could compromise the security of endpoint devices. These risks can stem from multiple sources, including malware, phishing attacks, software vulnerabilities, and insider threats.
Effective identification of endpoint risks enables organizations to prioritize their security efforts and allocate resources accordingly. By understanding the potential threats, organizations can implement targeted security controls and measures to mitigate the most significant risks. This proactive approach helps prevent successful cyberattacks and minimizes the impact on business operations.
For instance, identifying the risk of malware infections can lead to the implementation of antivirus software and regular security updates. Similarly, recognizing the threat of phishing attacks can result in employee training programs to raise awareness ands. By identifying and understanding potential risks, organizations can make informed decisions to safeguard their endpoints and protect against costly security breaches.
In conclusion, the identification of potential risks to endpoints is a fundamental step in endpoint risk management. It provides a clear understanding of the threat landscape, allowing organizations to prioritize security measures, allocate resources effectively, and proactively protect their endpoint devices from cyber threats.
Assessment: Evaluating the likelihood and impact of identified risks.
Risk assessment plays a critical role in endpoint risk management by providing a comprehensive understanding of the potential threats and their severity. It involves evaluating the likelihood of a risk occurring and the potential impact it could have on the organization. Effective risk assessment enables organizations to prioritize their security efforts, allocate resources efficiently, and make informed decisions about implementing appropriate security controls. Here are some key facets of risk assessment in endpoint risk management:
- Identification of threats and vulnerabilities: The first step in risk assessment is to identify the potential threats and vulnerabilities that could affect endpoints. This involves understanding the threat landscape, analyzing endpoint configurations, and identifying common attack vectors.
- Likelihood analysis: Once the threats and vulnerabilities have been identified, the likelihood of each risk occurring should be assessed. This involves considering factors such as the prevalence of the threat, the availability of exploits, and the organization’s specific security posture.
- Impact analysis: The next step is to evaluate the potential impact of each risk. This involves considering the potential consequences of a successful attack, such as data loss, disruption of operations, or reputational damage.
- Prioritization of risks: Based on the likelihood and impact analysis, risks should be prioritized to determine which ones pose the greatest threat to the organization. This prioritization process helps organizations focus their resources on addressing the most critical risks.
By effectively assessing risks, organizations can gain a clear understanding of their endpoint security posture and make informed decisions about implementing appropriate security controls. Risk assessment is an ongoing process that should be regularly reviewed and updated to reflect changes in the threat landscape and the organization’s security posture.
Mitigation: Implementing controls and measures to reduce the severity or likelihood of risks.
In endpoint risk management, mitigation involves implementing a range of controls and measures to reduce the severity or likelihood of identified risks. These controls and measures serve as safeguards to protect endpoint devices from potential threats and vulnerabilities, minimizing the impact of cyberattacks and ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of sensitive data.
-
Title of Facet 1: Access Control
Access control measures limit who can access endpoints and the actions they can perform. Examples include implementing strong passwords, multi-factor authentication, and role-based access controls. By restricting access to authorized users only, organizations can reduce the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.
-
Title of Facet 2: Software Updates and Patch Management
Regular software updates and patch management are crucial in mitigating risks associated with software vulnerabilities. By promptly applying security patches, organizations can fix known vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers. Automated patch management systems streamline this process, ensuring that endpoints are always up-to-date with the latest security fixes.
-
Title of Facet 3: Antivirus and Anti-Malware Software
Antivirus and anti-malware software detect and remove malicious software from endpoints. These solutions use various techniques to identify and block viruses, malware, ransomware, and other threats. By keeping antivirus and anti-malware software up-to-date and performing regular scans, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of malware infections.
-
Title of Facet 4: Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR)
EDR solutions provide advanced threat detection and response capabilities for endpoints. They use advanced techniques such as machine learning and behavioral analysis to identify and contain threats in real-time. EDR solutions empower organizations to quickly detect and respond to sophisticated cyberattacks, minimizing the potential damage.
By implementing a combination of these mitigation controls and measures, organizations can significantly reduce the severity or likelihood of endpoint-related risks. A well-rounded mitigation strategy is essential for protecting endpoints from evolving cyber threats and ensuring the overall security of the organization’s IT infrastructure.
Monitoring: Continuously tracking and observing endpoints for suspicious activities or vulnerabilities.
In endpoint risk management, monitoring plays a pivotal role in ensuring the continuous protection of endpoints from potential threats and vulnerabilities. It involves the use of various tools and techniques to track and observe endpoints for suspicious activities or vulnerabilities that could indicate a potential security breach or compromise. Effective monitoring enables organizations to detect and respond to threats in a timely manner, minimizing the impact on business operations and safeguarding sensitive data.
As a critical component of endpoint risk management, monitoring provides several key benefits:
- Early Detection of Threats: Continuous monitoring allows organizations to identify potential threats at an early stage, before they can cause significant damage. By detecting suspicious activities or vulnerabilities, security teams can take prompt action to investigate and mitigate the risks.
- Enhanced Threat Visibility: Monitoring provides comprehensive visibility into the security posture of endpoints, enabling organizations to understand the current threat landscape and identify patterns or anomalies that could indicate a potential attack.
- Improved Response Time: Real-time monitoring enables organizations to respond to threats quickly and effectively. By detecting and addressing security incidents in a timely manner, organizations can minimize the potential impact and prevent further damage.
Endpoint monitoring can be implemented using a combination of tools and techniques, including:
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems collect and analyze data from various sources, including endpoints, to identify suspicious activities and security incidents.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) solutions provide advanced threat detection and response capabilities, using techniques such as machine learning and behavioral analysis to identify and contain threats in real-time.
- Vulnerability scanners regularly scan endpoints to identify potential vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers.
By implementing effective endpoint monitoring practices, organizations can significantly enhance their overall security posture. Continuous monitoring provides early detection of threats, improves threat visibility, and allows for rapid response to security incidents, enabling organizations to protect their endpoints and safeguard sensitive data from evolving cyber threats.
Response: Taking appropriate actions to address and contain threats or incidents.
In endpoint risk management, response refers to the actions taken to address and contain threats or incidents that may compromise the security of endpoints. A prompt and effective response is crucial to minimize the impact of security breaches and maintain the integrity of sensitive data.
-
Title of Facet 1: Incident Response Plan
An incident response plan outlines the steps to be taken in the event of a security incident. It defines roles and responsibilities, communication channels, and containment procedures. Having a well-defined incident response plan enables organizations to respond quickly and effectively, reducing the potential damage caused by an attack.
-
Title of Facet 2: Threat Hunting and Analysis
Threat hunting involves proactively searching for and identifying potential threats that may not be detected by traditional security tools. By analyzing network traffic, endpoint data, and other sources, organizations can identify and neutralize threats before they cause significant damage. Threat hunting capabilities enhance the overall response strategy, enabling organizations to stay ahead of evolving cyber threats.
-
Title of Facet 3: Containment and Isolation
When a security incident occurs, it is crucial to contain and isolate the affected endpoints to prevent the spread of malware or unauthorized access. This may involve disconnecting infected endpoints from the network, restricting user access, or shutting down affected systems. Timely containment measures help minimize the impact of the incident and facilitate effective remediation.
-
Title of Facet 4: Remediation and Recovery
Once the threat has been contained, organizations need to remediate the affected endpoints and restore them to a secure state. This may involve removing malware, patching vulnerabilities, or restoring data from backups. A well-defined remediation plan ensures that endpoints are restored to full functionality while minimizing the risk of re-infection.
By implementing a comprehensive response strategy that encompasses these facets, organizations can effectively address and contain threats or incidents, minimizing the impact on endpoint security and maintaining the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of sensitive data.
Recovery: Restoring systems and data to a functional state after an incident.
Recovery is a critical component of endpoint risk management, ensuring that systems and data can be restored to a functional state after an incident. A successful recovery process minimizes the impact of a security breach and helps organizations maintain business continuity.
Endpoint risk management involves implementing strategies and practices to identify, assess, mitigate, and monitor risks associated with endpoint devices. Recovery plays a vital role in this process by providing a means to restore affected endpoints and data in the event of a security incident. Effective recovery capabilities enable organizations to quickly recover from attacks, reducing downtime and data loss.
For instance, if an endpoint is infected with malware, recovery measures may involve isolating the infected system, removing the malware, and restoring data from backups. A well-defined recovery plan ensures that these steps are executed efficiently, minimizing the impact of the incident on the organization’s operations.
Moreover, recovery is essential for maintaining regulatory compliance. Many regulations require organizations to have a disaster recovery plan in place to ensure the availability and integrity of critical data. By implementing robust recovery capabilities as part of endpoint risk management, organizations can demonstrate compliance and avoid potential legal liabilities.
In summary, recovery is a crucial aspect of endpoint risk management, enabling organizations to restore systems and data to a functional state after an incident. Effective recovery capabilities minimize downtime, reduce data loss, and ensure regulatory compliance, ultimately contributing to the overall security and resilience of the organization.
Endpoint Risk Management FAQs
Frequently asked questions and answers on endpoint risk management, a crucial aspect of cybersecurity.
Question 1: What is endpoint risk management?
Endpoint risk management involves identifying, assessing, mitigating, monitoring, and recovering from risks associated with endpoint devices connected to a network, such as laptops, desktops, smartphones, and IoT devices. It aims to protect these devices from unauthorized access, data breaches, malware infections, and other threats.
Question 2: Why is endpoint risk management important?
Effective endpoint risk management protects sensitive data, maintains regulatory compliance, and minimizes the impact of cyberattacks, ensuring business continuity and reducing financial and reputational damage.
Question 3: What are the key components of endpoint risk management?
Key components include identifying potential risks, assessing their likelihood and impact, implementing mitigation controls like firewalls and antivirus software, continuously monitoring endpoints for suspicious activities, and having a response plan for incidents like data breaches or malware infections.
Question 4: What are common endpoint risks?
Common endpoint risks include malware infections, phishing attacks, software vulnerabilities, insider threats, and unauthorized access.
Question 5: How can organizations improve their endpoint risk management posture?
Organizations can strengthen their endpoint risk management by implementing endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools, conducting regular security audits, providing employee security awareness training, and staying updated on the latest threats and vulnerabilities.
Question 6: What are best practices for endpoint risk management?
Endpoint risk management best practices involve implementing a layered security approach, enforcing strong password policies, using multi-factor authentication, patching software regularly, and backing up data regularly.
Summary:
Endpoint risk management is crucial for protecting organizations from cyber threats. By understanding the key components, common risks, and best practices, organizations can effectively safeguard their endpoints and maintain business continuity.
Transition to the next article section:
Implementing Endpoint Risk Management: A Comprehensive Guide
Endpoint Risk Management Tips
Endpoint risk management is a critical aspect of cybersecurity, safeguarding organizations from threats targeting endpoint devices such as laptops, desktops, smartphones, and IoT devices. Here are several tips to enhance your endpoint risk management strategy:
Tip 1: Implement a Layered Security Approach
Employ multiple layers of security controls, including firewalls, intrusion detection systems, antivirus software, and endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools, to create a comprehensive defense system against cyber threats.
Tip 2: Enforce Strong Password Policies
Implement strong password policies that require complex passwords, regular changes, and two-factor authentication to prevent unauthorized access to endpoints and sensitive data.
Tip 3: Regularly Patch Software and Operating Systems
Stay up-to-date with the latest software and operating system patches to fix vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers. Configure automatic updates whenever possible to ensure timely patching.
Tip 4: Conduct Regular Security Audits
Periodically conduct security audits to identify vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and compliance gaps in your endpoint security infrastructure. Address the findings promptly to strengthen your endpoint risk management posture.
Tip 5: Provide Employee Security Awareness Training
Educate employees on cybersecurity best practices, such as recognizing phishing emails, avoiding suspicious links, and reporting security incidents. This training empowers employees to become active participants in endpoint risk management.
Summary:
By implementing these tips, organizations can significantly enhance their endpoint risk management posture, protect against cyber threats, and ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of their data.
Transition to the article’s conclusion:
Endpoint risk management is an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring, adaptation, and collaboration. By adopting a comprehensive approach and incorporating these tips, organizations can effectively safeguard their endpoints and mitigate the risks posed by evolving cyber threats.
Endpoint risk management
Endpoint risk management plays a pivotal role in protecting organizations from the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats. By implementing a comprehensive approach that encompasses identification, assessment, mitigation, monitoring, and response, organizations can effectively safeguard their endpoints and sensitive data.
Effective endpoint risk management requires a layered security approach, regular patching of software and operating systems, and ongoing employee training. Organizations must also stay abreast of emerging threats and vulnerabilities to adapt their strategies accordingly. By adopting a proactive and collaborative approach, organizations can mitigate endpoint risks, maintain regulatory compliance, and ensure business continuity in the face of persistent cyber challenges.
Youtube Video:
