Cybersecurity incident handling refers to the procedures and practices used to detect, analyze, contain, and recover from cyberattacks or data breaches. It involves a systematic approach to managing cybersecurity incidents, minimizing their impact, and restoring normal operations.
Cybersecurity incident handling is crucial for organizations to protect their sensitive data, maintain business continuity, and comply with regulatory requirements. Effective incident handling helps organizations respond quickly and effectively to cyberattacks, reducing the potential for damage and reputation loss.
The field of cybersecurity incident handling has evolved significantly over the years, driven by the increasing sophistication of cyber threats and the growing reliance on digital technologies. Organizations now have access to a wide range of tools and services to help them detect, investigate, and respond to cyberattacks.
Cybersecurity incident handling
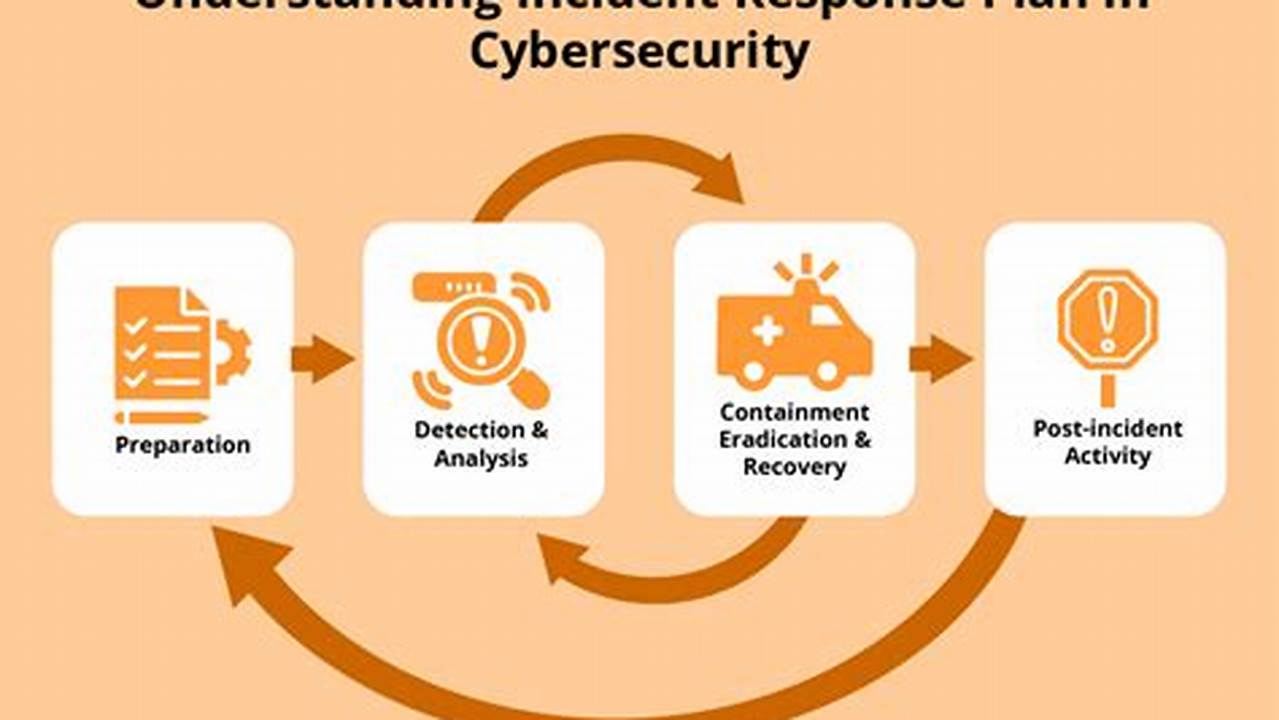
Cybersecurity incident handling is a critical aspect of protecting organizations from cyberattacks and data breaches. It involves a systematic approach to detecting, analyzing, containing, and recovering from cybersecurity incidents.
- Detection: Identifying and recognizing a cybersecurity incident.
- Analysis: Determining the nature and scope of the incident.
- Containment: Limiting the impact of the incident and preventing further damage.
- Recovery: Restoring normal operations and repairing any damage caused by the incident.
- Communication: Keeping stakeholders informed about the incident and its impact.
- Collaboration: Working with internal and external resources to respond to the incident.
- Learning: Analyzing the incident to identify lessons learned and improve future incident handling capabilities.
- Prevention: Implementing measures to reduce the risk of future incidents.
These key aspects of cybersecurity incident handling are interconnected and essential for organizations to effectively respond to and recover from cyberattacks. By understanding and implementing these aspects, organizations can minimize the impact of cybersecurity incidents and protect their sensitive data and systems.
Detection
Detection is the first and most critical step in cybersecurity incident handling. It involves identifying and recognizing that a cybersecurity incident has occurred. This can be a challenging task, as cybersecurity incidents can take many forms and can be difficult to distinguish from normal network activity.
There are a number of tools and techniques that can be used to detect cybersecurity incidents, including intrusion detection systems (IDS), security information and event management (SIEM) systems, and vulnerability scanners. However, the most effective way to detect cybersecurity incidents is to have a well-trained and experienced security team that is constantly monitoring the network for suspicious activity.
The importance of early detection cannot be overstated. The sooner a cybersecurity incident is detected, the sooner it can be contained and the less damage it can cause. In some cases, early detection can even prevent an incident from causing any damage at all.
Here are some examples of real-life cybersecurity incidents that were detected and handled effectively:
- In 2013, the Target Corporation detected a cybersecurity incident within hours of it occurring. This allowed them to quickly contain the incident and minimize the damage caused.
- In 2016, the Equifax credit reporting agency detected a cybersecurity incident within days of it occurring. This allowed them to quickly notify affected customers and take steps to protect their data.
These examples show the importance of early detection in cybersecurity incident handling. By understanding the connection between detection and cybersecurity incident handling, organizations can improve their ability to respond to and recover from cyberattacks.
Analysis
Analysis is a critical component of cybersecurity incident handling. It involves determining the nature and scope of the incident, which is essential for developing an effective response plan.
The analysis phase typically begins with collecting and examining evidence from the affected systems. This may include log files, network traffic data, and system configuration files. The goal is to identify the root cause of the incident and to determine its impact on the organization.
Once the nature and scope of the incident have been determined, the incident response team can develop a plan to contain the incident and mitigate its impact. This plan may include steps such as isolating infected systems, patching vulnerabilities, and restoring data from backups.
The following are some examples of real-life cybersecurity incidents that were successfully handled through effective analysis:
- In 2017, the WannaCry ransomware attack infected hundreds of thousands of computers worldwide. However, many organizations were able to mitigate the impact of the attack by quickly analyzing the incident and developing a response plan.
- In 2018, the Marriott International hotel chain suffered a data breach that exposed the personal information of millions of guests. Marriott was able to quickly contain the breach and minimize the damage by conducting a thorough analysis of the incident and implementing a comprehensive response plan.
These examples show the importance of effective analysis in cybersecurity incident handling. By understanding the connection between analysis and cybersecurity incident handling, organizations can improve their ability to respond to and recover from cyberattacks.
Containment
Containment is a critical aspect of cybersecurity incident handling as it aims to limit the impact of a cybersecurity incident and prevent further damage to an organization’s systems and data.
- Identifying and isolating affected systems: One of the first steps in containment is to identify and isolate affected systems to prevent the spread of the incident. This may involve taking systems offline, blocking network access, or restricting user privileges.
- Patching vulnerabilities: If a vulnerability is identified as the root cause of the incident, it is crucial to patch the vulnerability as soon as possible to prevent further exploitation.
- Implementing additional security controls: Additional security controls, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and anti-malware software, can be implemented to strengthen the organization’s defenses and prevent similar incidents from occurring in the future.
- Monitoring and logging: Continuous monitoring and logging of systems and network activity can help organizations detect and respond to incidents more quickly and effectively.
Effective containment measures can significantly reduce the impact of a cybersecurity incident and prevent further damage to an organization’s systems and data. By understanding the connection between containment and cybersecurity incident handling, organizations can improve their ability to respond to and recover from cyberattacks.
Recovery
Recovery is a critical aspect of cybersecurity incident handling as it involves restoring normal operations and repairing any damage caused by a cybersecurity incident. This can be a complex and time-consuming process, but it is essential for organizations to recover from an incident and minimize its impact.
- Restoring normal operations: Once the incident has been contained, the next step is to restore normal operations as quickly as possible. This may involve recovering data from backups, rebuilding systems, and reconfiguring networks.
- Repairing any damage: In addition to restoring normal operations, it is also important to repair any damage caused by the incident. This may involve patching vulnerabilities, replacing compromised systems, and restoring lost data.
- Testing and validation: Before returning systems to production, it is important to thoroughly test and validate them to ensure that they are operating correctly and that the incident has not left any lingering vulnerabilities.
- Reviewing and improving: Once the recovery process is complete, it is important to review the incident and identify any areas where the organization’s response could be improved. This may involve updating incident response plans, improving training, or implementing new security controls.
Effective recovery measures can help organizations minimize the impact of a cybersecurity incident and restore normal operations as quickly as possible. By understanding the connection between recovery and cybersecurity incident handling, organizations can improve their ability to respond to and recover from cyberattacks.
Communication
Communication is a critical aspect of cybersecurity incident handling as it involves keeping stakeholders informed about the incident and its impact. This is important for several reasons:
- Transparency and trust: Open and transparent communication with stakeholders helps build trust and credibility. By keeping stakeholders informed, organizations can demonstrate that they are taking the incident seriously and are committed to resolving it quickly and effectively.
- Reduced panic and misinformation: Effective communication can help reduce panic and misinformation among stakeholders. By providing accurate and timely information, organizations can prevent rumors and speculation from spreading, which can further damage the organization’s reputation and operations.
- Improved decision-making: Stakeholders need accurate information to make informed decisions about their response to the incident. Clear and concise communication can help stakeholders understand the risks involved and take appropriate steps to protect themselves and their assets.
Organizations should develop a communication plan that outlines who will be responsible for communicating with stakeholders, what information will be communicated, and how often updates will be provided. The communication plan should be tailored to the specific needs of the organization and the incident.
Real-life examples
There are several real-life examples of organizations that have successfully communicated with stakeholders during cybersecurity incidents.
- In 2013, the Target Corporation was the victim of a major data breach. Target quickly notified stakeholders about the breach and provided regular updates on the investigation and recovery process. This transparent communication helped Target maintain the trust of its customers and stakeholders.
- In 2016, the Equifax credit reporting agency was the victim of a data breach that exposed the personal information of millions of Americans. Equifax was criticized for its slow and ineffective communication with stakeholders. This lack of communication damaged Equifax’s reputation and led to a loss of trust among its customers.
Practical significance
The practical significance of understanding the connection between communication and cybersecurity incident handling is that it can help organizations improve their response to cybersecurity incidents. By developing a communication plan and communicating effectively with stakeholders, organizations can reduce the impact of cybersecurity incidents and protect their reputation and operations.
Collaboration
Collaboration is a critical aspect of cybersecurity incident handling as it involves working with internal and external resources to respond to the incident effectively. This can include collaborating with other departments within the organization, such as IT, legal, and public relations, as well as with external resources, such as law enforcement, cybersecurity vendors, and insurance companies.
- Sharing information: Collaboration enables organizations to share information about the incident with other stakeholders, such as law enforcement, cybersecurity vendors, and insurance companies. Sharing information can help to identify the source of the incident, develop mitigation strategies, and prevent similar incidents from occurring in the future.
- Coordinating response efforts: Collaboration can also help organizations to coordinate their response efforts with other stakeholders. This can involve coordinating the investigation, containment, and recovery efforts, as well as communicating with stakeholders and the public about the incident.
- Accessing specialized resources: External resources, such as cybersecurity vendors and law enforcement, can provide organizations with specialized resources and expertise that may not be available internally. This can include access to advanced cybersecurity tools, forensic investigators, and legal advice.
- Maintaining stakeholder confidence: Collaboration can also help organizations to maintain stakeholder confidence during a cybersecurity incident. By working with internal and external stakeholders, organizations can demonstrate that they are taking the incident seriously and are committed to resolving it quickly and effectively.
By understanding the connection between collaboration and cybersecurity incident handling, organizations can improve their ability to respond to and recover from cybersecurity incidents. Collaboration can help organizations to share information, coordinate response efforts, access specialized resources, and maintain stakeholder confidence.
Learning
Learning from cybersecurity incidents is a critical aspect of improving an organization’s overall cybersecurity posture. By analyzing incidents, organizations can identify weaknesses in their security controls, improve their detection and response capabilities, and prevent similar incidents from occurring in the future.
- Identifying root causes: Analyzing incidents can help organizations identify the root causes of the incident, such as vulnerabilities in software or misconfigurations in security settings. This information can then be used to implement targeted measures to address the root causes and prevent similar incidents from occurring in the future.
- Improving detection and response capabilities: Incident analysis can also help organizations improve their detection and response capabilities. By understanding how the incident occurred and how it was detected, organizations can improve their security monitoring and incident response plans to be more effective in the future.
- Developing training and awareness programs: Incident analysis can also be used to develop training and awareness programs for employees. By understanding the types of incidents that occur and the techniques used by attackers, organizations can develop more effective training programs to help employees prevent and detect cybersecurity incidents.
- Updating security policies and procedures: Incident analysis can also be used to update security policies and procedures. By understanding the weaknesses that were exploited in the incident, organizations can update their security policies and procedures to be more effective in preventing and detecting similar incidents in the future.
By understanding the connection between learning from cybersecurity incidents and improving cybersecurity incident handling capabilities, organizations can improve their overall cybersecurity posture and reduce the risk of future incidents.
Prevention
Prevention is a critical aspect of cybersecurity incident handling as it involves implementing measures to reduce the risk of future incidents occurring. This is essential for organizations to protect their sensitive data and systems from cyberattacks and to ensure business continuity.
- Identifying and mitigating vulnerabilities: One of the most important aspects of prevention is identifying and mitigating vulnerabilities in software, systems, and networks. This can be done through regular security audits, vulnerability assessments, and patch management.
- Implementing strong security controls: Implementing strong security controls, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and access control lists, can help prevent unauthorized access to systems and data.
- Educating employees about cybersecurity: Educating employees about cybersecurity best practices, such as strong password management and recognizing phishing emails, can help reduce the risk of human error leading to a cybersecurity incident.
- Developing and practicing incident response plans: Developing and practicing incident response plans can help organizations respond quickly and effectively to cybersecurity incidents, minimizing their impact.
By understanding the connection between prevention and cybersecurity incident handling, organizations can improve their overall cybersecurity posture and reduce the risk of future incidents.
FAQs on Cybersecurity Incident Handling
Cybersecurity incident handling is a critical aspect of protecting organizations from cyberattacks and data breaches. It involves a systematic approach to detecting, analyzing, containing, and recovering from cybersecurity incidents. This FAQ section addresses common concerns and misconceptions about cybersecurity incident handling.
Question 1: What is the importance of cybersecurity incident handling?
Cybersecurity incident handling is crucial for organizations to protect their sensitive data, maintain business continuity, and comply with regulatory requirements. Effective incident handling helps organizations respond quickly and effectively to cyberattacks, reducing the potential for damage and reputation loss.
Question 2: What are the key steps involved in cybersecurity incident handling?
The key steps in cybersecurity incident handling include detection, analysis, containment, recovery, communication, collaboration, learning, and prevention.
Question 3: How can organizations improve their cybersecurity incident handling capabilities?
Organizations can improve their cybersecurity incident handling capabilities by implementing a comprehensive incident response plan, conducting regular training and drills, and using automated tools for detection and response.
Question 4: What are the common challenges in cybersecurity incident handling?
Common challenges in cybersecurity incident handling include detecting and identifying incidents, understanding the scope and impact of incidents, and coordinating a timely and effective response.
Question 5: How can organizations prevent cybersecurity incidents from occurring?
Organizations can prevent cybersecurity incidents by implementing strong security controls, such as firewalls and intrusion detection systems, educating employees about cybersecurity best practices, and keeping software and systems up to date.
Question 6: What are the legal and regulatory requirements related to cybersecurity incident handling?
Organizations must comply with various legal and regulatory requirements related to cybersecurity incident handling, such as data breach notification laws and privacy regulations.
By understanding these key questions and answers, organizations can gain a better understanding of cybersecurity incident handling and its importance in protecting their assets and reputation.
Transition to the next article section…
Cybersecurity Incident Handling Tips
Cybersecurity incident handling is a critical aspect of protecting organizations from cyberattacks and data breaches. Here are some tips to help organizations improve their cybersecurity incident handling capabilities:
Tip 1: Develop a comprehensive incident response plan
An incident response plan outlines the steps that organizations should take in the event of a cybersecurity incident. The plan should include roles and responsibilities, communication protocols, and procedures for detection, containment, recovery, and communication.
Tip 2: Conduct regular training and drills
Regular training and drills help organizations prepare for and respond to cybersecurity incidents. Training should cover topics such as incident detection, containment, and recovery. Drills help organizations test their incident response plans and identify areas for improvement.
Tip 3: Use automated tools for detection and response
Automated tools can help organizations detect and respond to cybersecurity incidents more quickly and effectively. These tools can monitor networks for suspicious activity, detect and block malware, and automate incident response tasks.
Tip 4: Share threat intelligence with other organizations
Sharing threat intelligence with other organizations can help organizations stay informed about the latest cybersecurity threats and trends. This information can help organizations identify and mitigate vulnerabilities in their own systems.
Tip 5: Keep software and systems up to date
Keeping software and systems up to date is one of the most important things organizations can do to prevent cybersecurity incidents. Software updates often include security patches that fix vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers.
Summary:
- By following these tips, organizations can improve their cybersecurity incident handling capabilities and reduce the risk of cyberattacks and data breaches.
- Cybersecurity incident handling is an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring, training, and improvement.
Investing in cybersecurity incident handling is essential for organizations to protect their sensitive data, maintain business continuity, and comply with regulatory requirements.
Organizations should consider these tips and take proactive measures to enhance their cybersecurity incident handling capabilities and protect their assets from cyber threats.
Conclusion
Cybersecurity incident handling is a critical aspect of protecting organizations from cyberattacks and data breaches. It involves a systematic approach to detecting, analyzing, containing, and recovering from cybersecurity incidents. This comprehensive process helps organizations minimize the impact of cyberattacks, maintain business continuity, and comply with regulatory requirements.
Organizations must prioritize cybersecurity incident handling by developing robust incident response plans, conducting regular training, and leveraging automated tools. Effective incident handling requires collaboration, information sharing, and continuous learning to enhance an organization’s overall cybersecurity posture. By investing in cybersecurity incident handling capabilities, organizations can proactively address cyber threats and protect their sensitive data and systems.
Youtube Video: